5.3. Monopoly
Introduction
- Features of a Monopoly Market:
- Many buyers and only one seller in the market.
- Goods offered by the monopoly has no close substitutes.
- Large barrier to enter or exit the market.
- Monopolies are price makers.
- Why Monopolies Arise?
- The fundamental cause of monopoly is barriers to entry. A monopoly remains the only seller in its market because other firms cannot enter the market and compete with it.
- Monopoly resources: A key resource required for production is owned by a single firm.
- Government regulation: The government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce some good or service.
- The production process: A single firm can produce output at a lower cost than can a larger number of firms (Natural Monopoly) (Economies of Scale).
Monopoly Demand Curve
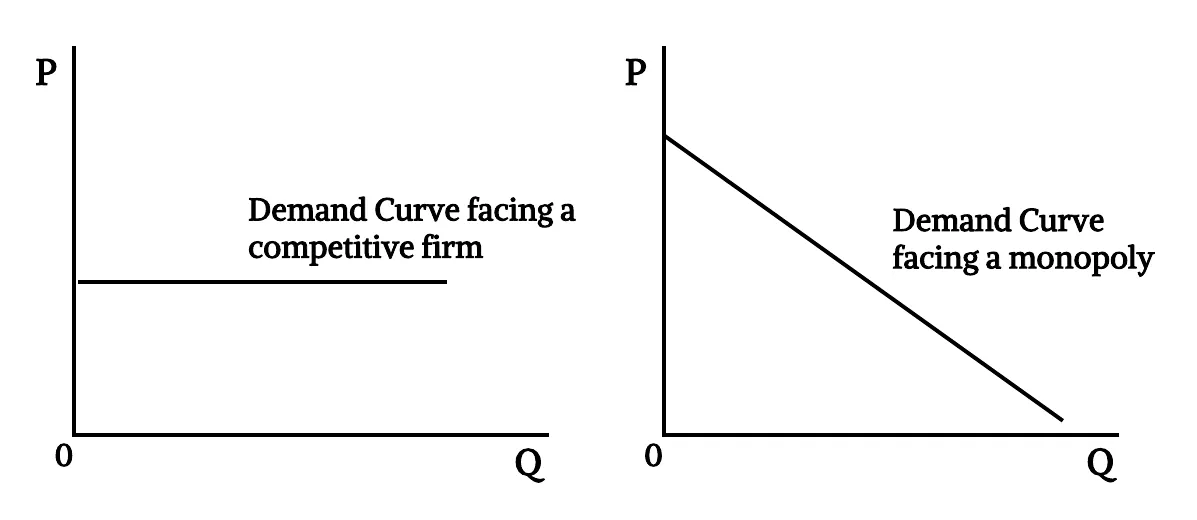
- Key difference between a competitive firm & a Monopoly is the ability to influence market price. It comes from the difference of the demand curve they face.
- Because a competitive firm can sell as much or as little as it wants at the market price, the competitive firm faces a horizontal demand curve at that price.
- Because a monopoly is the sole producer in its market, its demand curve is simply the market demand curve. Thus, the monopolist faces a downward sloping demand curve.
Monopoly Marginal Revenue
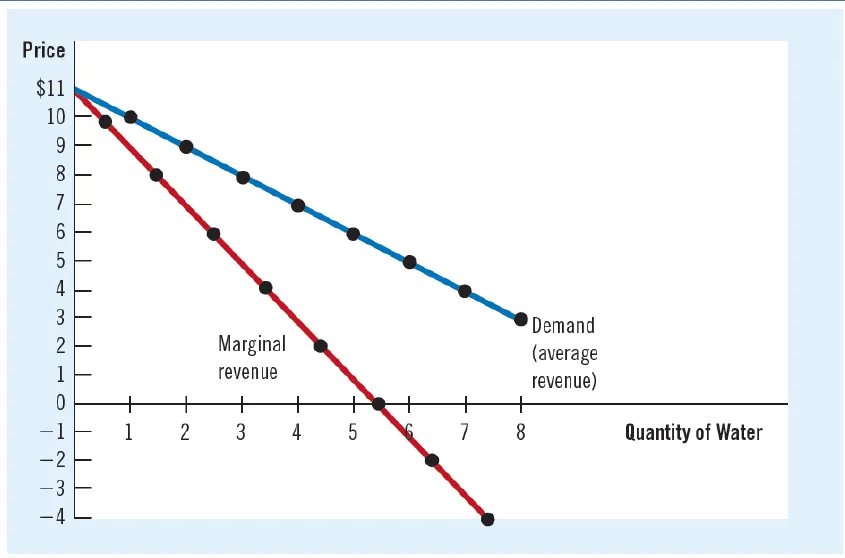
- A monopolist’s marginal revenue is less than the price of its good, P > MR.
- Marginal revenue on all units after the first is less than the price.
- Thus, a monopoly’s marginal - revenue curve lies below its demand curve.
- Demand & MR of monopoly:
- Price & Production:
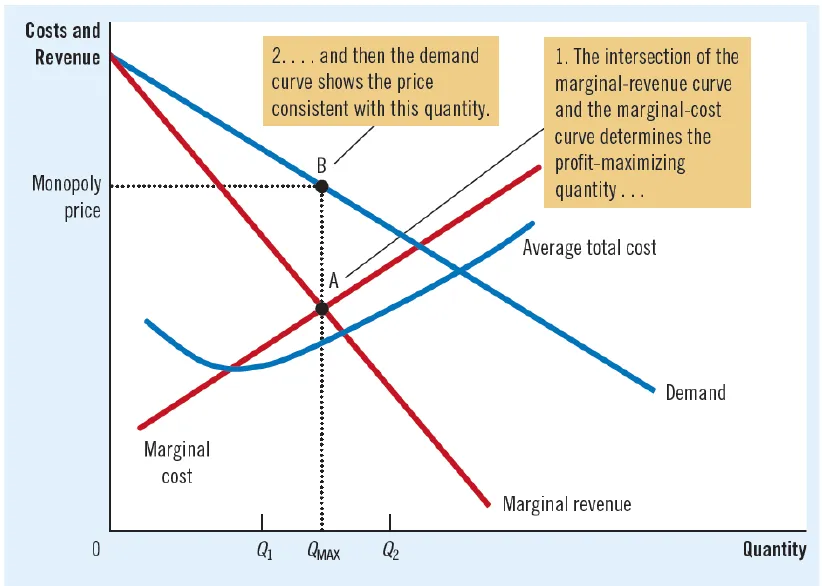
- Profit Maximizing quantity of output is found where MR=MC.
- Price is found from the demand curve at that quantity.
- Here, P>MR & MR=MC.
- Monopoly Profit:
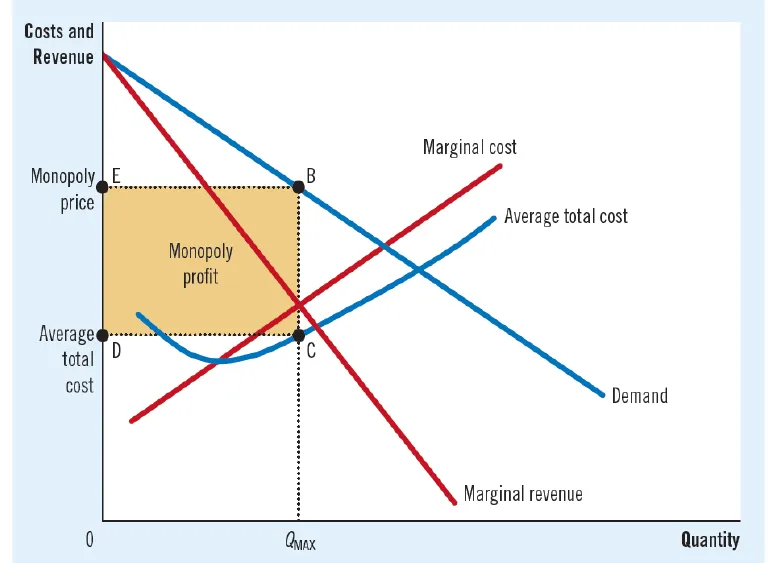
- Profit = (P-ATC)Q.
- Monopoly has the ability of earning positive economic profit in short run & in long run.
- Loss Making Monopoly:
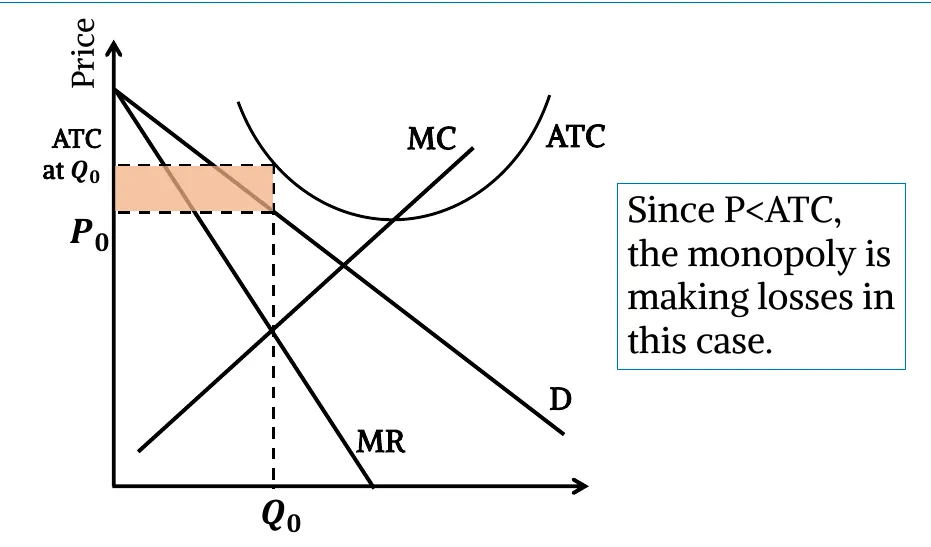
- Welfare Cost & Inefficiency of Monopoly:
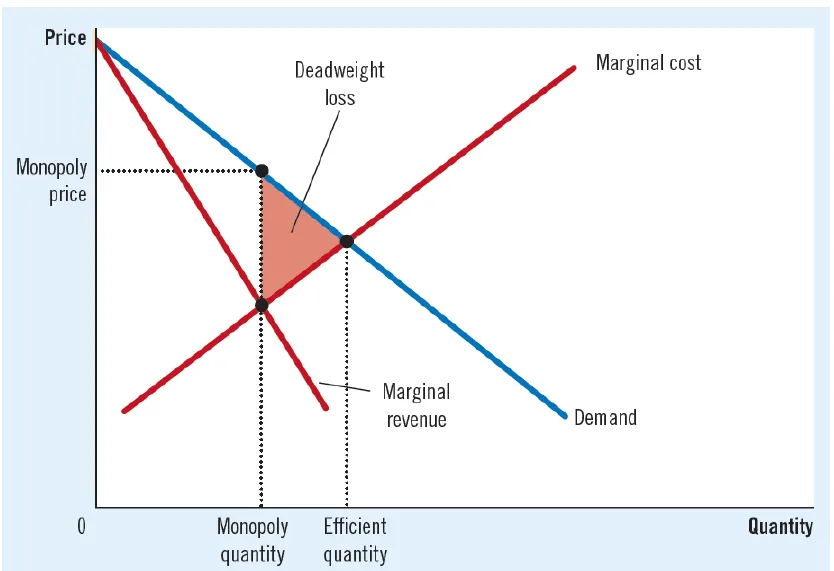
- A competitive market produces efficient quantity where demand & supply (MC) curve intersects & P=MC.
- But monopoly produces lower quantity where MR=MC but P>MC.
- Therefore, monopoly quantity is inefficient & monopoly generates a deadweight loss.